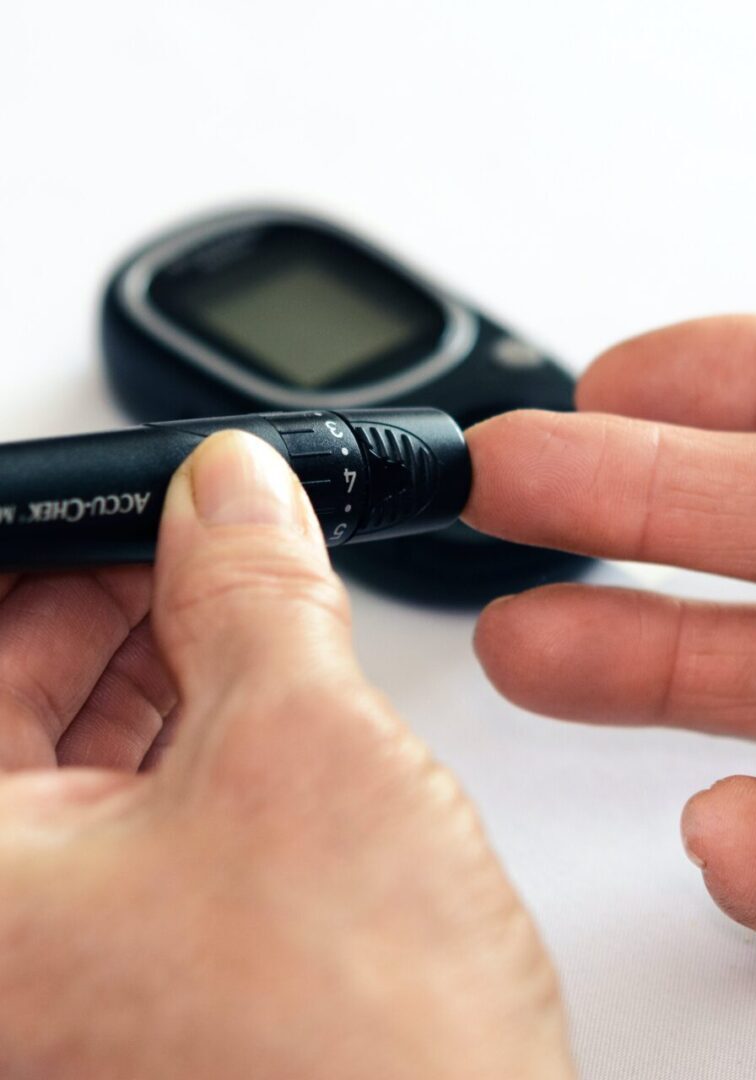
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body converts food into energy, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
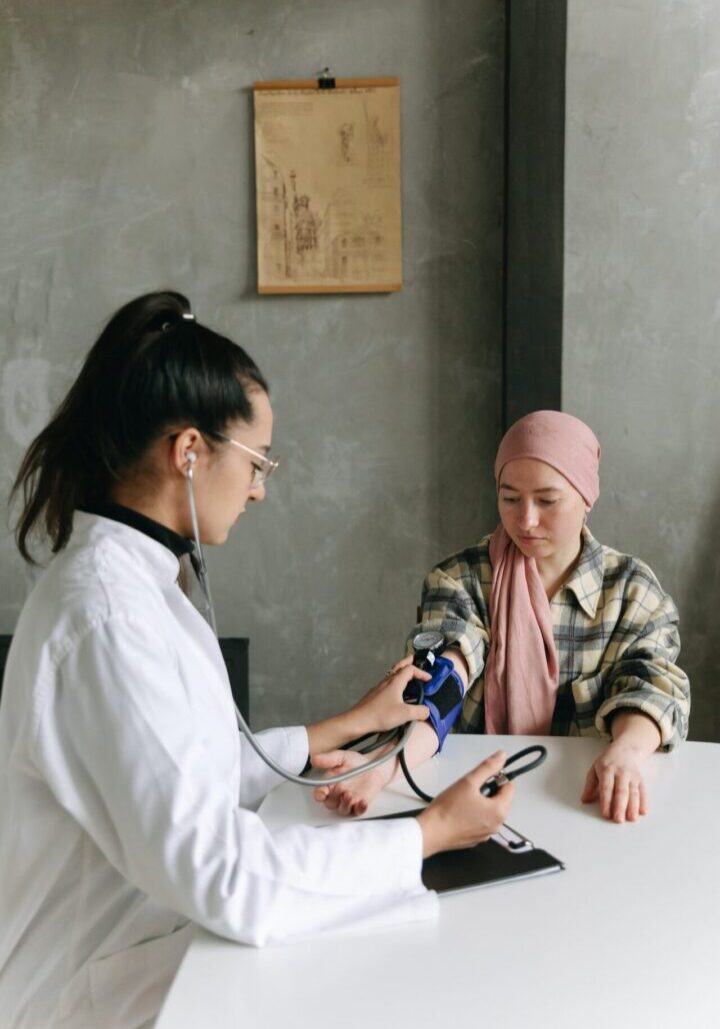

High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a serious chronic health condition characterized by consistently elevated blood pressure, posing a risk of vital organ damage, including the eyes, brain, heart, and kidneys. It often occurs without noticeable symptoms but increases the likelihood of cardiovascular complications.

High cholesterol is characterized by an excessive presence of fatty substances (cholesterol) in the blood. Typically caused by factors such as a diet high in fats, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, smoking, alcohol consumption, and hereditary influences, high cholesterol increases the risk of heart problems and stroke by potentially blocking blood vessels. Notably, it often presents no symptoms, requiring a blood test for diagnosis.

Obesity, characterized by abnormal or excessive fat accumulation, poses health risks arising from an imbalance between calories consumed and expended. Influenced by changes in dietary and physical activity patterns due to environmental shifts, obesity can lead to serious health complications, including diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and kidney problems.

Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleeping disorder characterized by repetitive pauses or slowing of breathing during sleep. This condition can lead to reduced oxygen supply to vital organs such as the brain, heart, lungs, and kidneys, inducing chronic stress. The primary types are obstructive sleep apnea, central sleep apnea, and complex sleep apnea syndrome. Obstructive sleep apnea, the most common type, involves relaxation of throat muscles, while central sleep apnea results from inadequate signals from the brain to control breathing. Complex sleep apnea, or treatment-emergent central sleep apnea, is a combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnea.
